Establishing new biotech research facilities. Development of a new biotech laboratory complex in Shenzhen.
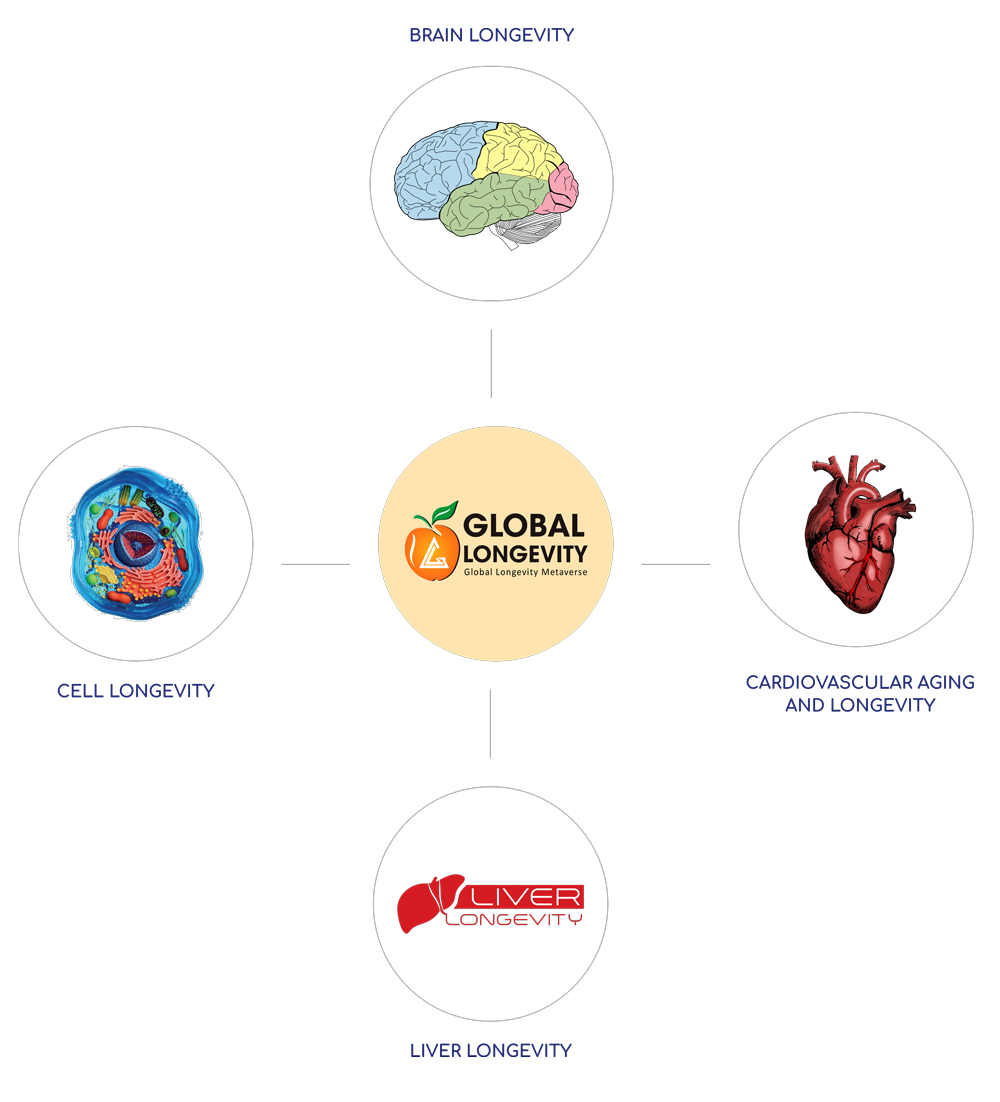
GLOBAL LONGEVITY METAVERSE
CONTINENTS
COUNTRIES
INVESTORS
PARTNERS
EMPLOYEES
I decided to live forever. And so far everything goes well.
Unknown Author
Global Longevity Labs
Our mission is to restore cell health and resilience through cell rejuvenationto reverse disease, injury and the disabilitiesthat can occur throughout life.
Diagnosis and Treatment
A complete diagnosis of the body means a comprehensive examination, which is carried out with the help of special devices and through the delivery of various tests. The data obtained allow us to make a complete picture of the state of human health, its internal organs and new formations, both benign and malignant.
Global Longevity Science Foundation
Adding Years to Our Lives and Life to Our Years Global Longevity Science Foundation (GLSF) is a global nonprofit working diligently to prevent chronic and age-related disease, aiming to extend the healthy human lifespan by funding critical scientific research.
Pharmacological Products
This industry is related to research, development, mass production, market research and distribution of medicines, mainly intended for the prevention, relief and treatment of diseases. Currently, the pharmaceutical industry is one of the most successful industries.
Organic Food Products for GLOBAL LONGEVITY
All over the world, the production of organic food is booming. This food contains on average 10–50% more vitamins, minerals and other nutrients compared to products produced by modern technologies. Organic food improves health, boosts immunity, and especially it is useful for children, pregnant women and nursing mothers.
Name:
Ticker:
Platform:
Token Type:
Hard Cap:
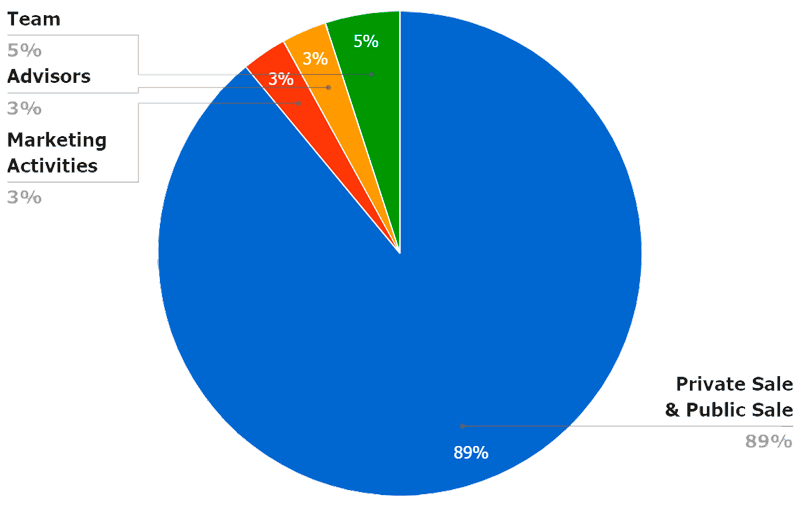
PERCENTAGE OF TOKENS DISTRIBUTION
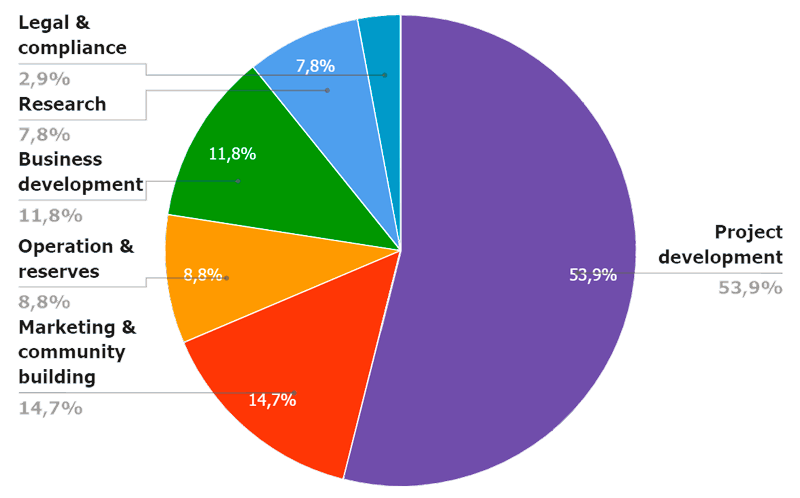
ALLOCATING AND USING FUNDS



Listing of Global Longevity Metaverse tokens on new world exchanges.

Development of the main directions of scientific research work of the Global Longevity Metaverse and the beginning of the work of the International Clinic of Global Longevity Metaverse.
Development and Improvement of GLOBAL LONGEVITY METAVERSE University.

Development and Improvement of GLOBAL LONGEVITY METAVERSE Television.